How Resonate works
OK, so now that you know why Resonate is useful, let's dive into how it works.
Checkpoints and replays
Have you heard the term "Durable Execution"? It means that an application workflow/function can resume from where it left off after the hosting process has disappeared (i.e. crashed, restarted, etc.).
The most practical way to achieve this, so that there is a coherent and sequential flow to code that the developer writes, is by checkpointing and replaying.
That is one of the things Resonate does. Resonate checkpoints at steps in your application code, basically whenever you use a Resonate SDK API. At each checkpoint Resonate saves some data to a datastore (database).
In Resonate, we call the checkpoints Durable Promises.
Resonate may execute a function many times using the stored data to reach the next step. The Durable Promise ID acting as a unique identifier for the checkpoint and idempotency key for the function execution. When the invoked function completes, the result is stored in the Durable Promise.
As the developer, you decide whether to invoke a local function, invoke a remote function, promisify an external system, and when to await the result — all of which is considered "durable" thanks to checkpointing and replaying.
Message passing
Each instance of a Resonate Worker (application node, microservice, etc.) runs in its own process. And each instance needs to be able to send and receive messages from a Resonate Server.
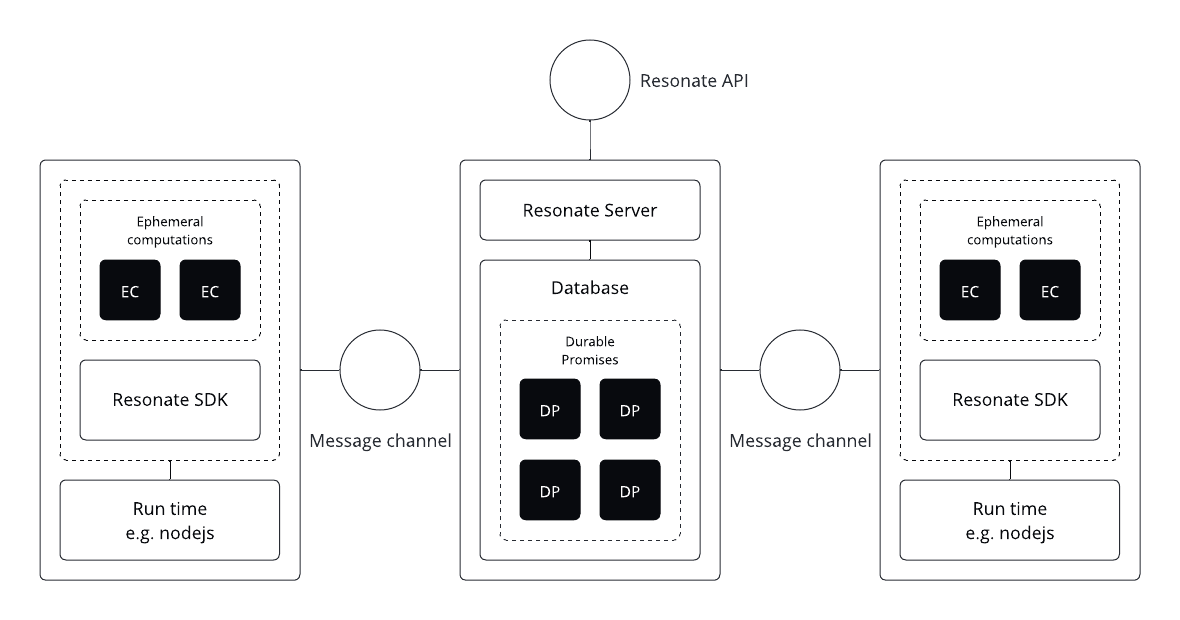
The protocol used to pass these messages is called Async RPC, and it is completely agnostic to the transport.
For example, Resonate can pass all its messages over HTTP APIs, or it can pass all its messages over Kafka queues, or some workers might receive on one transport and send on another.
The Async RPC protocol is designed to enable reliable and scalable communication between distributed processes, no matter the transport.
Resonate already has several transport plugins available and more are being developed.
Additionally, thanks to the protocol, Resonate offers built-in service discovery and load balancing.
When a worker or microservice connects to a Resonate Server, it registers itself both uniquely and as part of a group. This enables a Resonate Server to track which workers or microservices are available for a given function. It then load balances requests across them.